Contact Us:Email
prostatecure3d@gmail.com
Tel + 86-186-7321-6429
Prostate Dsease Causes
Prostate diseases are
usually caused by various causative pathogens and various prostatic
endotoxin. The most common pathogens
include two types of bacterial and non-bacterial. The most common
bacterial pathogens are staphylococcus,streptococcus, enterococcus,
escherichia coli, corynebacterium, proteus, klebsiella, etc. The
most common non-bacterial pathogens are virus, chlamydia,
mycoplasma, fungus, and trichomonas, etc. Prostatic endotoxin is the
harmful substances within the prostate, it can be divided into
exotoxin and endotoxin. Exotoxin refers to the external environment
pollution caused by harmful substances, such as food pollution.
Endotoxin refers to the human body in the metabolic process produces
harmful substances, such as uric acid.These harmful substances into
the prostate through different pathways.
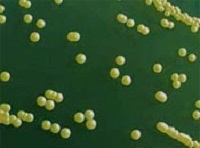
Prostate Disease and Pathogens
We found that all prostate diseases in the
development process, there are one or more specific pathogens. Like
Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus caused enlarged tonsil, and
Streptococcus bovis caused rectal cancer-like, in the patient's
prostate, we often can findthese bacteria. Some causative
pathogens can directly damage the prostate cells, and raise the
prostatic specific antigen( PSA) levels and may have a close
relationship with prostate cancer. After removing these pathogens,
the PSA value of a patient can return to normal with prostate
nodules disappearing. In the past 20 years, prostatitis patients who
have received our 3D Prostate Targeted Treatment rarely have suffered
from prostate cancer after removing the pathogens and infections.
As shown below:
The pathogens with
weak pathogenicity (such as staphylococcus,streptococcus,
enterococcus) are generally spread through the blood and
lymphatic way from other parts of the body (such as the upper
respiratory tract and intestinal) into the prostate. When the
body immunity is reduced, these pathogens multiply, will damage
the prostate. The pathogens with very strong pathogenicity (such
as sexually transmitted diseases pathogens) are generally
through direct diffusion from the urethra into the prostate.
Even a small number of these invasive causative pathogens, will
cause damage to the prostate.
The causative
pathogens release a variety of toxins, direct damage to prostate
cells, produces a variety of pathological cells, compromise
gland function, and the quality of semen. The prostate and vas
deferens tubes become blocked, and calcification form. Overtime
the prostate gland formed a variety of pathological tissues,
Such as infected tissue, hyperplastic tissue, and cancerous
tissue, etc.
These pathogens must
be identified through proper specimen sampling techniques so the
most effective treatment medications can be used for pathogen
clearance. However, many urologists and healthcare providers are
unable to properly identify the problem causing pathogens because of
(1) a lack of understanding of the biology necessary to obtain
accurate test result, and (2) inadequate or incorrect testing
methods. Unfortunately, the blind use of oral and systemic injection
medications to treat these conditions have become the treatment
standard. At the same time many healthcare providers refuse to
acknowledge the existence of causative pathogens. This results in
treatment failure and additional complications (side effects) from
the overuse and misuse of medications. In turn, this makes the
initial prostate diseases more complex and difficult to treat.
At our 3D Urology and Prostate Clinic we have overcome the problems
of testing and identifying causative pathogens. We have our own
biological laboratory. We use a full set of laboratory examination
and testing procedures in combination with our 3D Prostate Targeted
Treatment to accurately determine (1) the causative pathogens of
prostate disease, (2) the most effective treatment medications by
drug sensitivity testing, (3) the location of various lesion tissue
sites, and (4) the best treatment method to remove the causative
pathogens, clearing prostatic endotoxin and blockages and
calcification, and discharging harmful substances.
The Common Pathogens Of
Prostate Disease
The most common
pathogens include two types of bacterial and non-bacterial. The most
common bacterial pathogens are staphylococcus,streptococcus,
enterococcus, escherichia coli, corynebacterium, proteus,
klebsiella, etc. The most common non-bacterial pathogens are virus,
chlamydia, mycoplasma, fungus, and trichomonas, etc.
1) Causative gram-negative bacteria
include: Escherichia coli, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, etc. Causative gram-positive bacteria
include:Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Streptococcus viridans (SV),
Corynebacterium, etc. These bacteria are the most common bacteria
that cause
prostate disease and
complications.
2) Anaerobic bacteria
(anaerobicbacteria) is a kind of bacteria that grow better under
anaerobic conditions than in aerobic environment, it is widely
exists in the deep mucosal surface of skin and cavities. Because of
pelvic tissue (including prostate) is close to the rectum and anus,
can be easily infected by anaerobic bacteria. Prostate is relatively
deep in anatomy, and is relatively a closed anaerobic environment ,
anaerobic bacteria grow easily.
3) Fungus includes Candida and Yeast.
According to the areas which been infected by fungus, fungal
infection can be divided into superficial fungal disease and deep
fungal disease. Deep fungal disease can invade the human skin,
mucous membranes, deep tissue and internal organs, and even cause
systemic disseminated infection, and the causative pathogen is
mainly Candida albicans (candida Albicans). Candida albicans is the
most common pathogen that causes
prostate disease and
complications.
4) There are three type of
Chlamydia,
Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia pneumoniae and Chlamydia psittaci.
Chlamydia trachomonatis is one of the most common sexually
transmitted pathogens and it is also one of the most common causes
of urogenital infection. In males, Chlamydia causes urethritis,
prostatitis, epididymitis, sperm damage, and infertility, etc. In
females, Chlamydia causes cervicitis, endometritis, uterine
inflammation, hydrosalpinx, tubal scarring, fallopian tube
obstruction, natural abortion, tubal pregnancy, and infertility,
etc.
5) Among mycoplasma, Mycoplasma
hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum and genital mycoplasma are main
causes of urinary and reproductive tract infection.Ureaplasma
urealyticum causes urethritis, cervicitis, pelvic inflammatory
disease PID, endometritis, salpingitis, epididymitis and
prostatitis.
6) Some types of virus can cause
prostate disease and
complications, such as human papilloma
virus (HPV),Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Coxsackie Virus ( CSV) and Herpes
Simplex Virus (HSV). Virus will weaken immunity, and easily combined
with other pathogen infection. Virus can damage the urogenital
organs directly, and may result in prostate cancer.
Prostatic Endotoxin
Prostatic endotoxin
refers to harmful substances within the prostate. Prostatic
endotoxin is divided into exotoxin and endotoxin.
Exotoxin refers to
external environment pollution, such as, air pollution, water
pollution, and food pollution. Environment pollution brings harmful
chemical materials, such as, alkylating agent, polycyclic aromatic
hydrocarbons, aromatic amine compounds, nitroso compounds, amino azo
dyes, tobacco, food pyrolysis products (AIA), plant toxins, heavy
metal carcinogenic material like cadmium, and chemical drugs into
the prostate. Harmful materials in the external environment can
enter the prostate in different ways. These materials damage
prostate cells and tissues, and cause cancer.
Endotoxin refers to
harmful products created in the human body during the process of
metabolism. These harmful products include: lactic acid, ketone
acid, uric acid, and free radicals, which can accumulate in the
prostate through blood circulation, lymphatic circulation, bladder
function, and urine backflow. The free radical is the endotoxin that
causes the most serious prostate damage. Free radicals, and their
by-products (body oxidation reactions), play a major role in the
prostatic aging process. When prostatic proteins and DNA are
damaged, cell death and cancerous changes occur. Uric acid is one of
the principal materials that form prostatic calcification. Prostatic
endotoxin also includes: biological toxins produced by pathogenic
micro-organisms, excess fat, and old and dead cells within the
prostate. Prostate endotoxins are generally yellow. Prostatic
endotoxin can accumulate in the prostate through a variety of
channels into the prostate, such as rectal spread, blood
circulation, lymphatic circulation, and bladder urine backflow,etc .
These endotoxins damage prostatic cells and tissues, irritate the
urethra and nerves, and cause dysuria and male sexual dysfunction.
When prostatic endotoxins continuously deposit in the prostate, they
cause the prostate blockage, prostate calcification, and prostate
cancer.
|